This web page is created within BALTICS project funded from the European Union’s Horizon2020 Research and Innovation Programme under grant agreement No.692257.
Projekta FSR aktualitātes
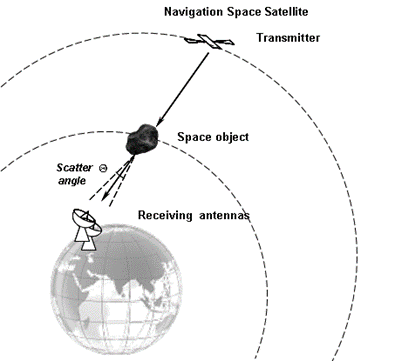
From December 2020, Ventspils International Radio Astronomy Centre (VIRAC) is implementing the scientific project “The application of the forward scatter radar method for the detection of space objects”, No. lzp-2020 / 2-0101. The project researches, develops and evolves new radar methods with the aim of accurately determining the location positions of asteroids and comets approaching Earth. One of the tasks of the project is to explore the application of a new and unique radar method based on radio wave scattering. This method is based on the applied effect that occurs when a bright celestial body illuminates the studied body, thus the energy is scattered along the line of sight forward, thus significantly increasing compared to the reflected energy. The developed method allows to detect space objects, regardless of its shape, material and radiation intensity. The “through-scattering” location method is implemented by combining radar VLBI technology and the scattering effect of electromagnetic radiation, involving bright space objects as transmitters in observations. By applying this method, the probability of detection of bodies that pose a threat to the Earth can be significantly increased, as well as the method allows to increase the observation distance at which the observation body would be identified. During the last four months, VIRAC researchers have been working on the detection of space objects using the “through-scattering” location method, thus evaluating the effectiveness of the method in an experimental way. By July 2021, more than 15 experimental sessions were performed using the Irbene radio telescope complex in single station mode and interferometer mode. RT-32 and RT-16 VIRAC radio telescopes (using 32-meter and 16-meter parabolic antennas, respectively) and 1.6 GHz frequency band receivers were used in the experiments. In Figure No.1 the scheme of the experiment is displayed. The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) GPS and Galileo satellites were used as radiation sources or transmitters in the experiments. During the experiments, using the “through-scattering” location method, observation lines “transmitter-receiver” (“transmitter” – a specific navigation satellite, “receiver” – Irbene radio telescopes) were created, thus space debris objects of different sizes were identified, as well as an International Space Station with a total geometric area of approximately 400 m2.

Ventspils Augstskolas Inženierzinātņu institūta “Ventspils Starptautiskais radio astronomijas centrs (VeA VSRC)” izplānotais - sagatavotais Latvijas Zinātnes Padomes (LZP) granta konkursa pieteikums Nr. lzp-2020/2-0101 “Radio lokācijas, balstīta uz radioviļņu izkliedes efektu, metodes pielietojums kosmosa objektu detektēšanai”/„The application of the forward scatter radar method for the detection of space objects” (FSR) ir ticis augstu novērtēts un finansiāli apstiprināts ar LZP 2020.gada 9.novembra lēmumu. Projekta mērķis ir izstrādāt metodiku, kas, apvienojot radioviļņu izkliedes efektu ar radara VLBI tehnoloģiju, spētu detektēt Zemei tuvojušos asteorīdus, komētas un kosmiskās atlūzas tuvajā Zemes telpā. Piedāvātā jaunā zinātniskā pieeja sniegs iespēju iegūt unikālus rezultātus, kas iegūti ar radar-detektēšanas tehniku, izmantojot bistatiskas sistēmas. Piedāvātās metodikas priekšrocība - tā var detektēt kosmosa objektus neatkarīgi no to formas un materiāla. Projektā tiks pētīts praktiskais pielietojums izstrādātajai metodei, kura veic novērojamā objekta koordinātu noteikšanu ar ļoti augstu precizitāti. Metodikas pārbaudē tiks iekļauta VLBI kompleksa kalibrācija, izmantojot gan dabiskus radio avotus, gan mākslīgos augsti orbitālos pavadoņus. Izstrādātā metode tiks pielietota, novērojot tuvās Zemes telpas objektus ar VSRC radioteleskopu kompleksu, tādejādi praktiski novērtējot metodes efektivitāti. Izstrādāto metodi varēs pielietot sistēmās, kas veic kosmisko draudu identificēšanu, un uzdevumos, kas saistīti ar kosmosa satiksmes organizēšanu pie arvien augošā objektu skaita. Projekta aktivitātes ir plānots īstenot laika posmā no 1.12.2020. līdz 31.12.2021., kopējais finansējums ir 100 389,00 eiro. Projektā kopumā ir plānots iesaistīt 5 zinātniskos darbiniekus, projekta vadītājs ir Ņižņijnovgorodas Radio fizikālā pētījuma institūta vadošais pētnieks Nikolajs Dugins, kurš ir jaunās metodikas autors un kuram ir vairāk kā 230 zinātniskās publikācijas un kompetence projekta pētījuma virzienos.


















