This web page is created within BALTICS project funded from the European Union’s Horizon2020 Research and Innovation Programme under grant agreement No.692257.
High-performance computing
High-performance computing (HPC)
– A computing industry, that deals with science and engineering tasks where computing demands are so high that calculations with conventional computers are not possible for everyday users. High-performance computing uses computers that are referred to as “super-computers”.
Studies in the High-Performance Computing Division focus on three main areas:
- Research in engineering physics
- Radio astronomical data processing and their methods
- Near space objects research
VIRAC research in engineering physics is related to the following application areas:
- Numerical hydrodynamics (CFD) and mechanics calculations (including the effect of wind flow on different types of objects, numerical models of engineering tools);
- Modelling of Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) phenomena;
- Application of physical field solving methods to support local industry, such as calculations of mechanical loads of individual components of newly developed products.
The HPC department process observation data for the following types of observations:
- single-dish observations;
- VLBI;
- radar-VLBI;
- complementary radar-VLBI and SLR (together with the University of Latvia Institute of Astronomy).
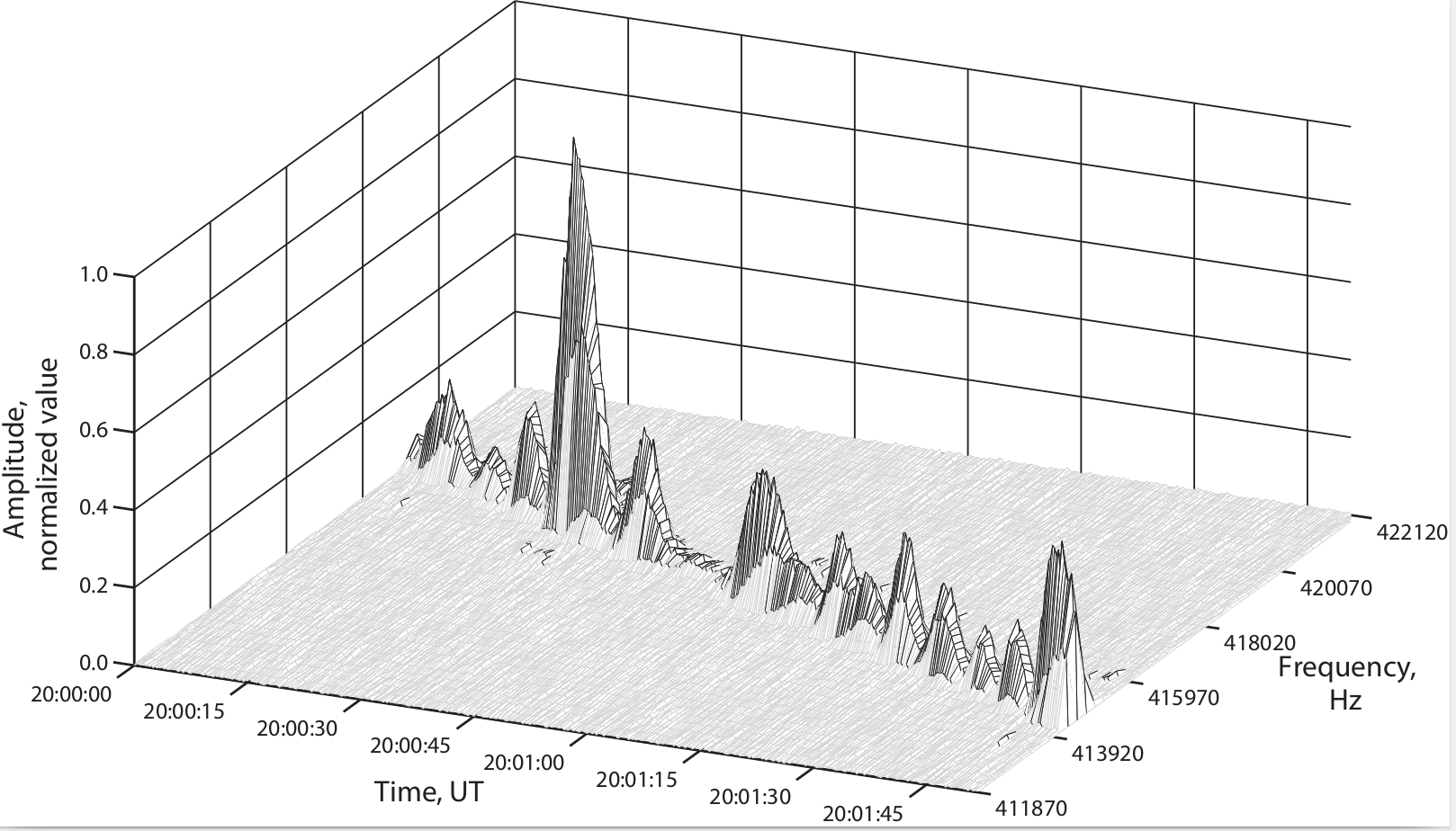
Within the framework of several project studies, the staff of the department performs improvements in data processing algorithms, including weak signal detection, FFT, wavelets and parallel algorithms in flexible code development using HPC.
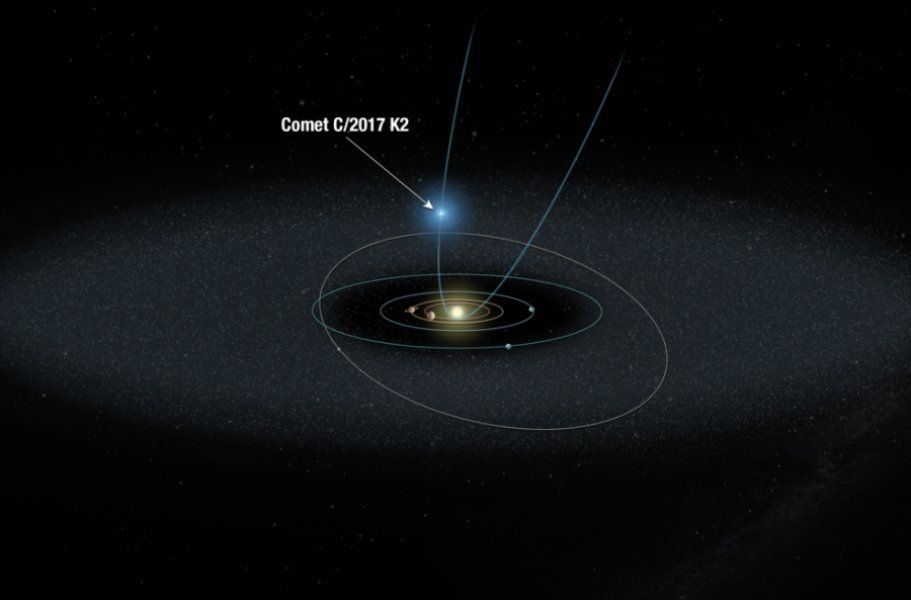
Comet C/2017 K2 (PANSTARRS) [2]
Near Space Research Topics:
- Radar-VLBI studies
- Complementary usage of Radar-VLBI and Satellite Laser Ranging
- Planetary Studies (Comets, Asteorids)
- Earthquake Research (satellites, space debris)