This web page is created within BALTICS project funded from the European Union’s Horizon2020 Research and Innovation Programme under grant agreement No.692257.
Remote Sensing and
Signal Discrete Processing
Remote sensing
is the science of obtaining information about objects, areas or phenomena and analysing data collected by devices that are not in direct contact with the object under investigation. One of its subfields is earth observation, which includes analysing photos and pictures of the Earth’s surface and other measurements acquired from remote sensing platforms such as aircraft and satellites with the goal to address a range of issues in environmental monitoring and national economy.
Applied earth observations performed by VIRAC researchers contribute to the following sectors of the national economy:
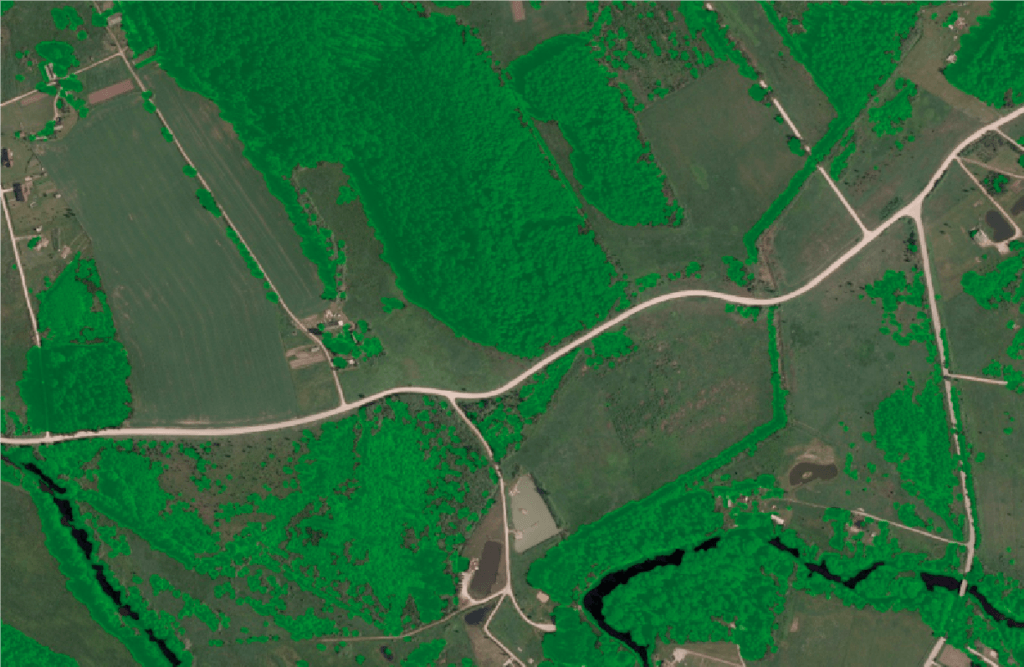
- Forest industry: monitoring forest resources and supporting national forest inventories through using satellite imagery, aerial photography and LIDAR data (identifying tree-crown cover, identifying individual trees and their crowns, classifying tree species, and estimating wood volume and biomass);
- Environment protection: oil-spill recognition in natural water bodies (primarily sea) using synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data;
- Urban development: mapping of urban environments (inventory and mapping of urban buildings and green /vegetation areas);
- Agriculture: precision agriculture (PA) or satellite farming.